Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
INTRODUCTION:
Polycystic ovary syndrome is characterized by
1. Anovulation (causing infertility, irregular or absent menstrual periods)
2. Hyperandrogenism (causing hirsutism, acne with elevated serum testosterone and androstenedione).
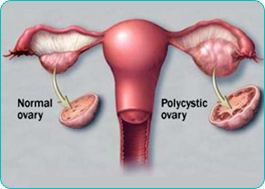
Patients with this syndrome may complain of abnormal bleeding, infertility, obesity, excess hair growth, hair loss and acne. In addition to the clinical and hormonal changes associated with this condition, vaginal ultrasound shows enlarged ovaries with an increased number of small (6-10mm) follicles around the periphery (Polycystic Appearing Ovaries or PAO).
While ultrasound reveals that polycystic appearing ovaries are commonly seen in up to 20% of women in the reproductive age range, PolyCystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is estimated to affect about half as many [or approximately 6-10% of women]. The condition appears to have a genetic component and those effected often have both male and female relatives with adult-onset diabetes, obesity, elevated blood triglycerides, high blood pressure and female relatives with infertility, hirsutism and menstrual problems.