Men's reproductive system
Sperm production
LH is responsible for the production of the male hormone testosterone, which along with FSH is responsible for stimulating sperm production in the testicles.
Sperm production [spermatogenesis], is a continuous process. It takes about 72 to 74 days for a male "germ" cell to develop into an active sperm. Several hundred million sperm are produced on a daily basis. From the millions of sperm cells available each day, only a small proportion has full fertilising potential.
Spermatogenesis is most efficient at a temperature of 34°C. It is vulnerable to increases in temperature.
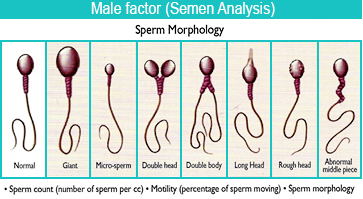
A sperm cell consists of two main parts:
- The head which has the crucial role of clinging to an egg and penetrating its outer membrane, taking with it its genetic information
- The tail, which enables the sperm cell to "swim" the length of the female reproductive tract to reach an egg.
Problems affecting any of these components will affect the fertilising power of the sperm cell.
Best time for conception
Becoming pregnant is not always straightforward even for people without fertility problems. Humans are one of the least fertile creatures on earth, with only a 15-25 % chance of conception each month.
Sperm can only live for around 48 hours in the female reproductive tract and the egg needs to be fertilised within 72 hours following ovulation, leaving a narrow window for fertilisation. Thus, the best time for conception is around the middle of the menstrual cycle just before ovulation occurs.
Pregnancy
Under normal circumstances only a few hundred of the 14 million sperm deposited naturally into the vagina during intercourse are able to reach the end of the fallopian tube where the egg can be fertilised.
After one sperm has successfully fertilised an egg, cell division begins and the fused cells become an embryo. Migration of the embryo happens at the same time and about a week following ovulation, the embryo finds itself in the uterus and implants itself into the endometrium. Successful implantation prevents the corpus luteum and endometrium from breaking down, therefore menstruation does not happen.
At this point, a third gonadotropin, the human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), is produced by the placenta which develops upon implantation. The hCG plays an important role in maintaining the pregnancy. It stimulates the corpus luteum to continue to produce high levels of oestrogen and progesterone.